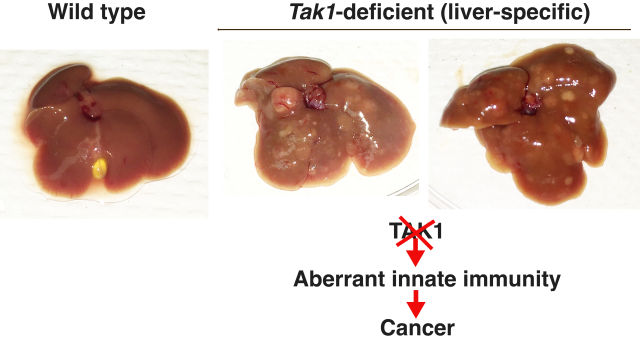
How aberrant innate immunity facilitates arising cancer stem cells

North Carolina State University
Jun Ninomiya-Tsuji
Liver cancers kill many people at a similar rate to that in decades ago, while survival rates are improving in many other cancers. Thus, developing preventive methods for liver cancers are highly anticipated. However, the mechanisms by which liver cancers are developed are still largely elusive. Our research focuses on a protein kinase, mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 7 (MAP3K7), known as TAK1, which has been implicated in multiple inflammatory signaling pathways in innate immunity. Interestingly, genetic ablation of TAK1 causes rapid hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) development with 10% penetrance in the mouse model, which closely resembles human HCC. This might indicate that aberrant innate immunity is a cause of HCC in animals including humans. In this project, we will define how aberrant TAK1 signaling causes HCC by focusing on the early phases of carcinogenesis including cancer stem cells.