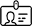MESSAGE FROM THE LAB
RESEARCH
Elucidation of control mechanisms on development and response of the immune system by cytokines
We are analyzing control mechanisms on development and response of the immune system from the viewpoint of IL-7 by using mutant mice.
 |
Functions of the IL-7 receptor in the immune systemIL-7 receptor (IL-7R) plays important roles in differentiation and maintenance of T cells. We are analyzing the mechanisms how IL-7R controls functions of T cells and DNA recombination of T cell receptor genes, in relation with immunometabolism and epigenetics. |
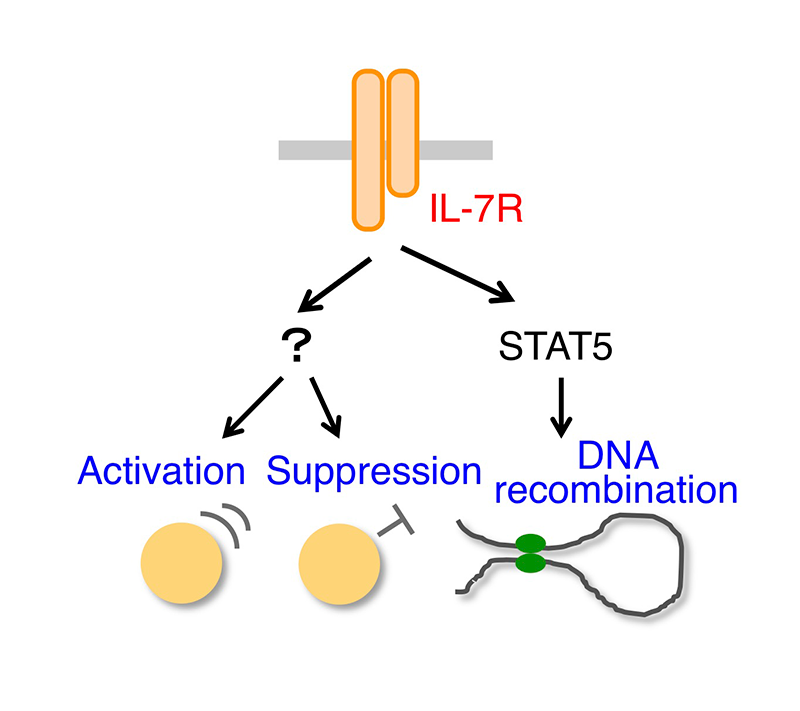
Regulation of IL-7 receptor expression during differentiation and response of immune cellsExpression of the IL-7R receptor (IL-7R) is strictly regulated during development and response of lymphocytes. We revealed that glucocorticoids, with strong immunosuppressive effects, controversially enhance immune response by diurnally controlling IL-7R expression and redistribution of T cells. We are investigating the crosstalk between the immune and endocrine systems and the circadian rhythm and sex difference of the immune system. |
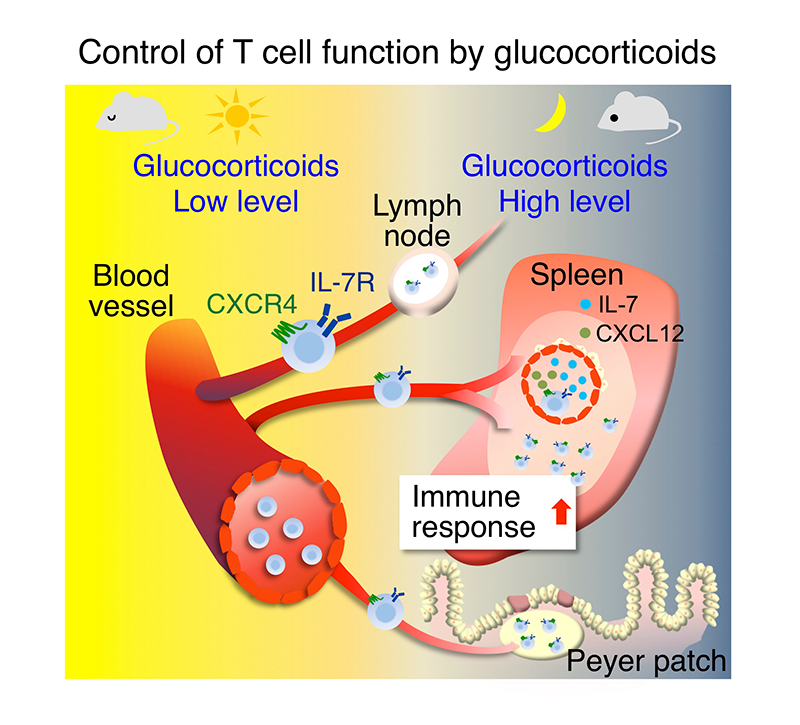 |
Visualization and local function of cytokine-producing cells and discovery of novel innate-like lymphocytesIn addition to lymphocytes, lymphoid tissues contain stromal cells that form the microenvironment supporting development and response of lymphocytes. We elucidate the immune microenvironment by analyzing cytokine-producing stromal cells. In addition, we analyze functions of novel innate-like lymphocytes which depend on tissue IL-15. |
 |
TOPICS
2020.7.10
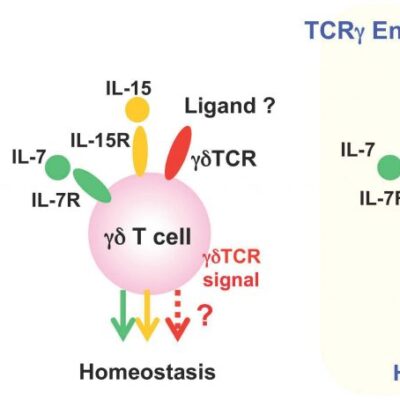
Requirement of TCR signal for γδ T cell homeostasis in peripheral organs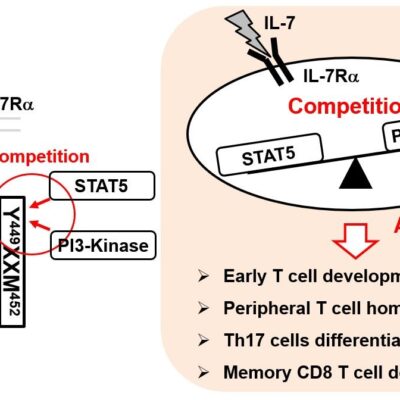
2020.7.7
Competition between STAT5 and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase under IL-7 receptor signaling modulates T cell development and homeostasis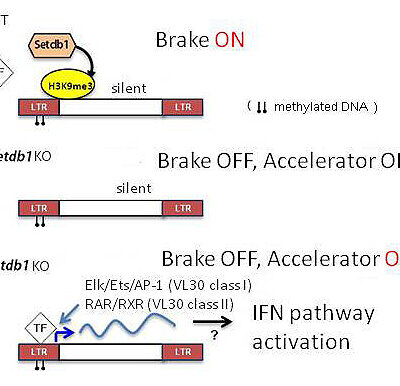
2018.5.9
A somatic role for the histone methyltransferase Setdb1 in endogenous retrovirus silencing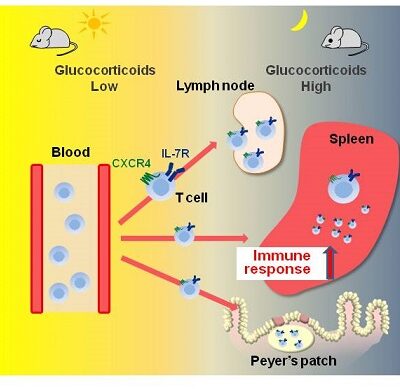
2018.2.7
Glucocorticoids drive diurnal oscillations in T cell distribution and responses by inducing interleukin-7 receptor and CXCR4